Cyber Threats on Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralised ledger, or list, of chronological transactions stored in a distributed network of connected computers or nodes. Each new set of transactions, called “block”, is recorded and cryptographically linked to the previous block, forming a chain. It works like a database (ledger) with some additional features as follows:
Depending on the specific application requirement, a blockchain can be (i) public (permissionless) where everyone can participate and join the network, or (ii) private (permissioned) where only a group of users or computers can join the blockchain network.
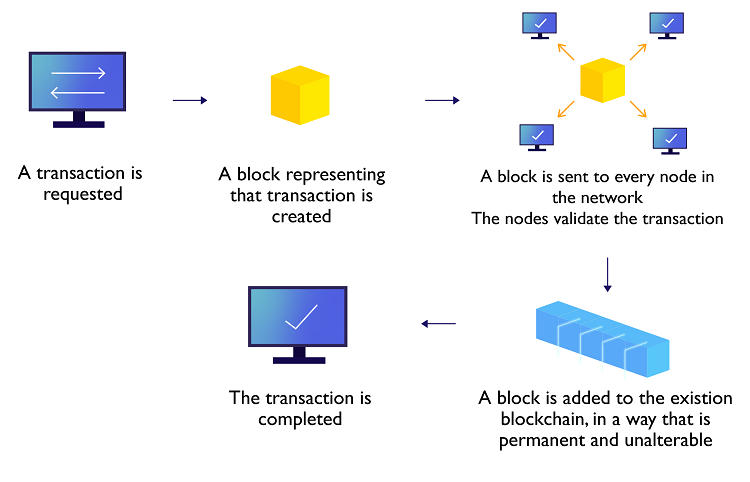
This emerging technology has attracted much attention in recent years and there are already quite some applications around the globe. In particular, there are some use cases in Hong Kong to enhance efficiency and the workflow in various business areas:
This nascent technology also helps reduce security threats from the traditional CIA (confidentiality, integrity and availability) security model perspective, except confidentiality:
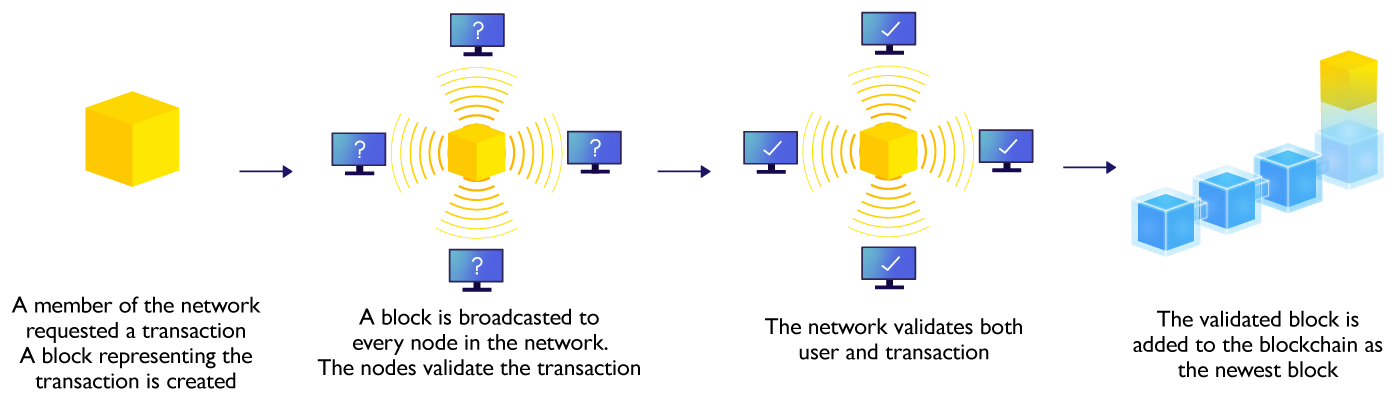
Other than enhanced security in integrity and availability, blockchain also provides features like transparency and pseudonymity:
While blockchain technology produces a tamper-proof transaction ledger, it should be noted that blockchain is not immune to all cyber attacks. Thorough governance, access control, system design, security controls, best practices and procedures in traditional systems should also be taken into account carefully when implementing blockchain applications. Some potential cyber threats or issues may be:
Below are some but not an exhausted list of security measures and controls to mitigate the risks in blockchain projects/systems.
Disclaimer: Users are also recommended to observe the disclaimer of this website and read the user agreements and privacy policies of the security software and tools before downloading and using them.
