Plan for Information Security
Information is a valuable asset to your business. The use of proper preventive measures and safeguards reduces the risk of successful security attacks, which might otherwise cost you a large fortune. Some losses might even be irrecoverable, e.g. the loss of a business deal due to a leakage of confidential information to a competitor.
With effective information security management, you are providing your company with the best strategy and a cost-effective solution for the overall protection of valuable information. The advantage is that it is easy-to-manage and, most importantly, minimises the risk of attacks and helps you to ultimately save costs. Safeguard these assets as best as you can. Make the security budget a mandatory part of your company / organisational budget.
Information security management involves a combination of prevention, detection and reaction processes. It is a cycle of iterative activities and processes that require ongoing monitoring and control.
Security Management Cycle
Information is one of the most valuable assets in your business. With an effective information security management policy in place, you will be able to provide your company with a strong security strategy, and a cost-effective solution for the overall protection of valuable information. The advantage is that information control becomes easier to manage and, most importantly, you can minimise the risk of attacks, ultimately saving costs. You want to safeguard your assets as best as you can, so simply making a security budget a mandatory part of your company / organisation budget would be a wise move.
Information security management involves a combination of prevention, detection and reaction processes. It is a cycle of iterative activities and processes that require ongoing monitoring and control. While this management cycle is mostly applied at the overall organisation level, it can also be applied to different functions or units in a business to prevent financial loss, e.g. the sales department, the customer service unit, and so on.
In order to make security management work, involvement, understanding and support from all members in your organisation is a crucial factor in the effectiveness of any program. Do not be fooled into thinking it is an isolated task just for the security or IT department.
The diagram below highlights the major activities involved in any security management cycle.
Security management cycle
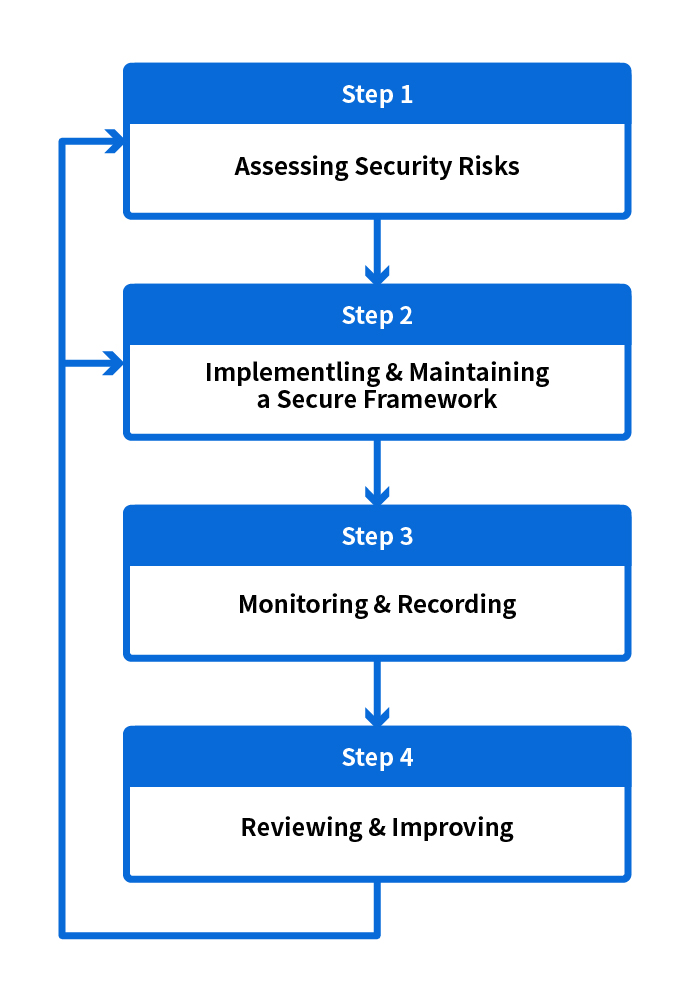
Step 1: Assessing Security Risks
Step 2: Implementing & Maintaining a Secure Framework
With implementation and maintenance being carried out to provide a secure framework, there is also the need for constant monitoring and recording so that proper arrangements can be made when tackling a security incident.
In addition, day-to-day operations such as users' access attempts and activities while using a resource, or information, need to be properly monitored, audited, and logged as well: e.g. individual user ID needs to be included in audit logs to enforce individual responsibility. Each user should understand his responsibility when using company resources and be accountable for his actions.
Major activities include:
Running hand-in-hand with all major activities and processes in the Security Management Cycle, (that is, Assessing Security Risks, Implementing & Maintaining a Secure Framework, and Monitoring & Recording) is Reviewing and Improving, which is an ongoing review that identifies what enhancements are necessary. This is a series of a cyclic compliance reviews and re-assessments designed to make sure that security controls are properly put into place to meet security requirements, and to cope with any rapid technological and environmental changes. It also requires continuous feedback and monitoring. The review can be done through periodic security audits to monitor and review security practices and strategies on an on-going basis.
Security Audit
A security audit is a repetitive checking process to ensure that security measures are properly implemented from time to time. A Security Audit is performed more frequently than a Security Risk Assessment. It aims to find out if the current environment is securely protected in accordance with the defined security policy.
Objectives of a Security Audit
Auditing Steps
Security Controls on Auditors
The security control compliance of auditors should be monitored and reviewed actively and periodically. The organisation must reserve the right to audit the responsibilities of auditors defined in the service level agreement, and have those audits carried out by an independent third party.
To ensure an effective and comprehensive review, detailed inventories should be maintained accurately and kept up-to-date, including:
